DNS
An application layer protocol defines how the application processes running on different systems, pass the messages to each other.
- DNS stands for Domain Name System.
- DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address.
- DNS is required for the functioning of the internet.
- Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots.
- DNS is a service that translates the domain name into IP addresses. This allows the users of networks to utilize user-friendly names when looking for other hosts instead of remembering the IP addresses.
- For example, suppose the FTP site at EduSoft had an IP address of 132.147.165.50, most people would reach this site by specifying ftp.EduSoft.com. Therefore, the domain name is more reliable than IP address.
DNS is a TCP/IP protocol used on different platforms. The domain name space is divided into three different sections: generic domains, country domains, and inverse domain.
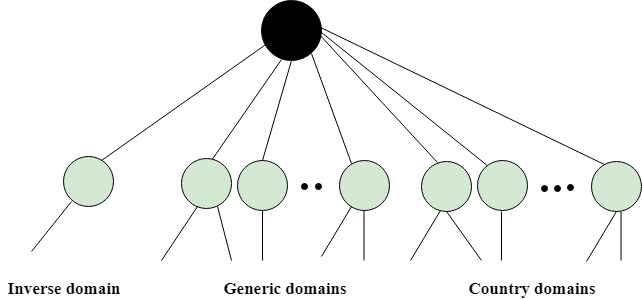
Generic Domains
- It defines the registered hosts according to their generic behavior.
- Each node in a tree defines the domain name, which is an index to the DNS database.
- It uses three-character labels, and these labels describe the organization type.
| Label |
Description |
| aero |
Airlines and aerospace companies |
| biz |
Businesses or firms |
| com |
Commercial Organizations |
| coop |
Cooperative business Organizations |
| edu |
Educational institutions |
| gov |
Government institutions |
| info |
Information service providers |
| int |
International Organizations |
| mil |
Military groups |
| museum |
Museum & other nonprofit organizations |
| name |
Personal names |
| net |
Network Support centers |
| org |
Nonprofit Organizations |
| pro |
Professional individual Organizations |

Country Domain
The format of country domain is same as a generic domain, but it uses two-character country abbreviations (e.g., us for the United States) in place of three character organizational abbreviations.
Inverse Domain
The inverse domain is used for mapping an address to a name. When the server has received a request from the client, and the server contains the files of only authorized clients. To determine whether the client is on the authorized list or not, it sends a query to the DNS server and ask for mapping an address to the name.
Working of DNS
- DNS is a client/server network communication protocol. DNS clients send requests to the. server while DNS servers send responses to the client.
- Client requests contain a name which is converted into an IP address known as a forward DNS lookups while requests containing an IP address which is converted into a name known as reverse DNS lookups.
- DNS implements a distributed database to store the name of all the hosts available on the internet.
- If a client like a web browser sends a request containing a hostname, then a piece of software such as DNS resolver sends a request to the DNS server to obtain the IP address of a hostname. If DNS server does not contain the IP address associated with a hostname, then it forwards the request to another DNS server. If IP address has arrived at the resolver, which in turn completes the request over the internet protocol.
Read also:
